OOP IN PHP FOURTH PART
THE KEYWORD $ THIS, SELF, PARENT AND STATIC

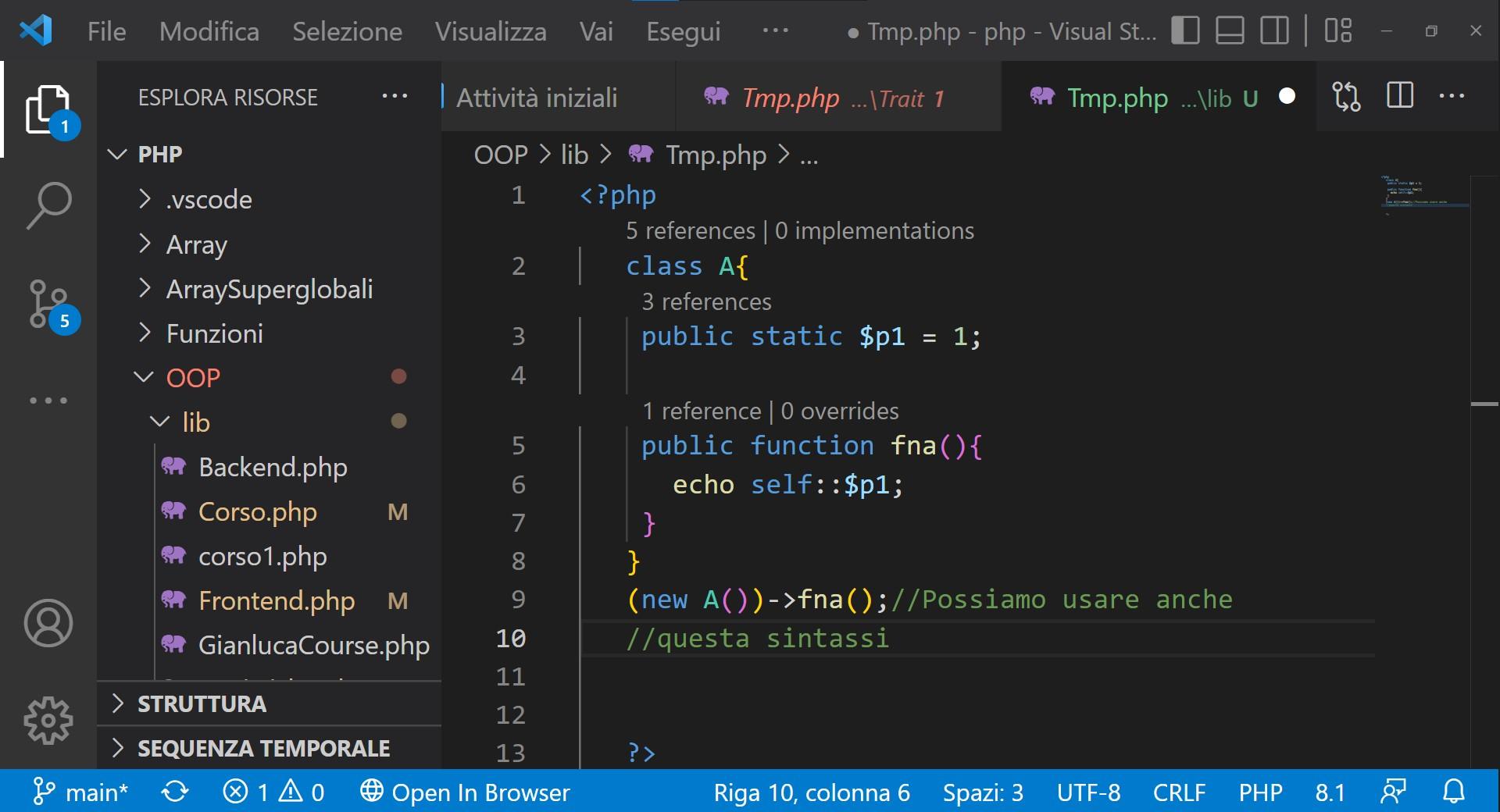
ACCESS METHODS WITH PARENT AND SELF KEYWORDS
The figure alongside shows an example of how to use the parent and self keywords.

With static we can refer not to the class itself but to the child class.
CREATE AN INSTANCE OF A CLASS WITH SELF AND STATIC
When we create the instance with the new keyword , the constructor is automatically invoked. If instead of making the constructor public we make it private what happens? If we try to create an instance outside the class we have a fatal error. If we declare a method as private or protected we cannot access it externally (from the global scoop). Only within the class can we create an instance.

This can be useful when we want to create a single instance of a certain class (singleton pattern). We can also return new static , the difference is in the context of inheritance, in this case that is, with static an object of the child class B is returned (see figure on the side).

DEEP AND SHALLOW COPY OF AN OBJECT
Let’s see how to copy an object, if we assign the object of a class to another variable, the copy does not take place as the assignment is by reference. Let’s see an example:
$obj1 = new stdClass () ;
$obj2 = $obj1;
var_dump($obj1, $obj2);

USER CLASS CREATION
Let’s create a User class in this way, the var_dump() is also shown below;


THE KEYWORD CLONE
We have two references to the same object, same ID, and same id and name properties. If we want to clone an object before assignment we use the keyword clone .
$user2 = clone $user1;
If we now do the var_dump() we have two different objects identified by different IDs.

If we modify the name property via $user2 we will have:


THE MAGICAL METHOD __CLONE
Now the problem is that we have the same id, the solution is to use a magic method. In fact, we can make two types of copies, a shallow copy and a deep copy. We use the magic __clone method invoked when creating the new object to create different ids .


Thanks to the magic method __clone we can make a copy in depth. Let’s create a new Skills class.


As for skillInstance we don’t have two different properties, Skills objects have the same identifier. We have two properties that point to the same object. So if we modify one of the two arrays, the modification will also be reflected in the other object. This is a shallow copy if we want to do a deep copy we have to resolve the references. This is the code:


SERIALIZE AND DESERIALIZE OBJECTS
Serialization is the transformation of complex data such as objects and arrays into strings. The following code serializes an array.

The array was not stored in the file as is but we have the serialized value, that is, it has been transformed into a string and stored in the file. When we go to read the information it is deserialized. The serialization process can also be performed on an object, using the serialize function. The unserialize function is used to deserialize the object, that is, passing it from a representation in the form of a string to an object.Let’s see what the serialized array looks like:

SERIALIZE THE USER OBJECT
Let’s see the code used to serialize objects:

We note that the IDs are different, we can do a Deep copy with this instruction:
$user2 = unserialize(serialize($user1));
We have two different objects after deep copy, modifying one will not affect the other.
INSTANCEOF, GET_CLASS AND ::CLASS
Let’s see the code that uses these three PHP instructions right away.
ANONYMOUS CLASSES
Since PHP 7 we also have anonymous classes. We work in an anonymous class as we do in a normal class, if we do a var_dump() in response we have an object of an anonymous class. When are anonymous classes used? We never have to say when we need a single object in a specific point of the application, instead of creating a special file, importing it and creating an instance, we do everything on the fly with an anonymous class. Another use is to simulate nested classes, even if they are not nested classes as they are in Java.

Leave A Comment